Background
Ikaros, encoded by IKZF1, is a critical transcriptional factor in the B cell development, and the oncogenic isoforms could contribute to leukemia transformation and poor outcome in B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). Truncated oncogenic isoforms lacking DNA binding domains could be originated from intragenic deletion and alternative splicing, and act as dominant-negative manner. Because of the variable transcripts and sequence homology of IKZF1, there are still challenges to identify the ikaros isoforms by traditional PCR.
Methods
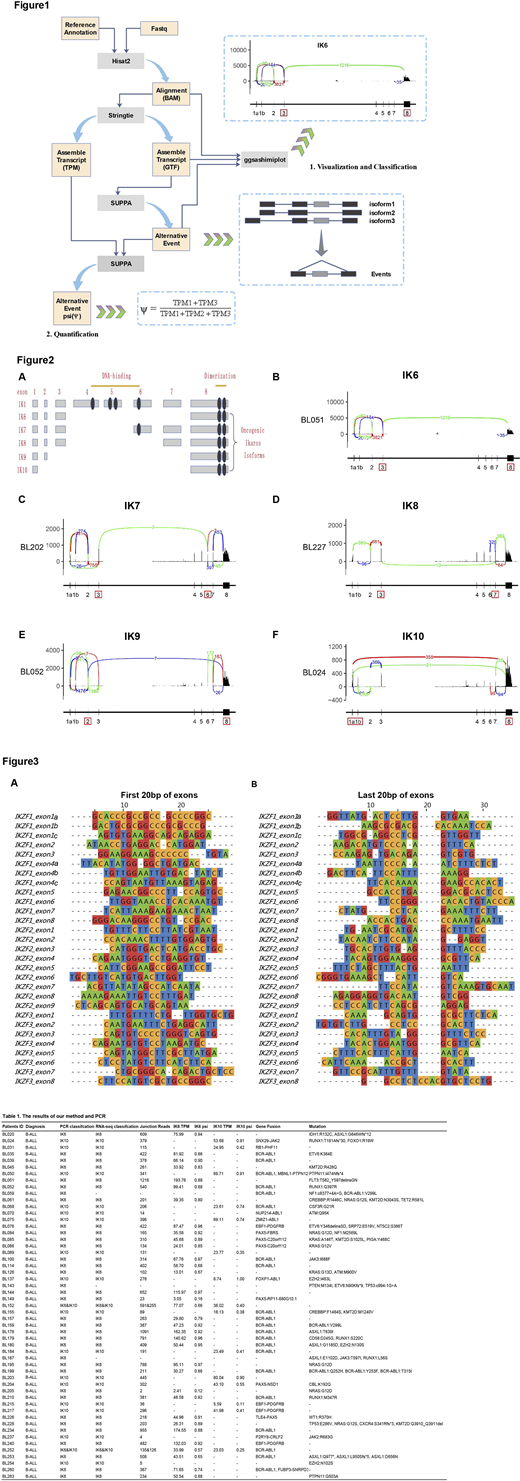
Here, we developed an integrated pipeline to adapt the classification and qualification of oncogenic ikaros isoforms. Reads were aligned to the reference using the Hisat2. The classification of ikaros isoforms can be visualized and inferred by counting the specific junction reads from ggsashimi plotting. Then we applied SUPPA to each annotation gtf generated by Stringtie to obtain the possible focal alternative splicing events and percentage spliced in (psi or ψ) denoting the abundance or fraction of the oncogenic isoforms (Figure 1).
Results
Oncogenic ikaros isoforms (Figure 2) were found in 20.2% (53 of 263 cases) BCP-ALL patients by PCR technology. The IK6 and IK10 transcripts accounted for 64% (32 of 53 cases) and 32% (16 of 53 cases), respectively, in addition to two patients harbored both IK6 and IK10 (Table 1). The truncated oncogenic transcripts of IKZF1 often occurred in Ph+ and Ph-like BCP-ALL, which always were characterized by JAK-STAT or RAS signaling activation. The BCR-ABL1 (40%), PAX5 rearrangement (11%), EBF1-PDGFRB (8%), and ABL1-class fusion (6%) were the most recurrently co-occurred gene fusions (Table 1). By the integrated pipeline for RNA-seq analysis, the sensitivity and the specificity have achieved 94.3% and 100% for IK6 and IK10. Intriguingly, although IK7, IK8 and IK9 have been seldom identified in BCP-ALL, we revealed that IK7, IK8 and IK9 were recurrently presented with low frequency by RNA-seq. In order to eliminate the impact of sequence homology to junction reads between exons, we aligned the first and last 20bp base of all exons of ikaros family genes and found low homology among them (Figure 3). Theoretically they were unlikely false positives caused by sequence mismatches, which were also evidenced by the presence of dim bands corresponding to the appropriate products from most PCR results, but further significance of those oncogenic transcripts with low frequency in BCP-ALL remains to be discovered, especially in relapse or refractory cases.
Discussion
Through the visualization of junction reads, we can easily infer the subtype of the oncogenic ikaros isoforms, which could also be extrapolated to other frequently truncated genes, such as ERG and BTK in BCP-ALL. Moreover, the revised SUPPA pipeline can quantify the expression level of oncogenic transcripts by the value of TPM and psi-value. In this study, we provide a paradigm to exquisitely classify and quantify alternative splicing transcripts through junction reads.
Keywords: B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia, isoforms, IK6, IK10, IKZF1
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal